Here’s some insights on a financial interim budget for a nation. With Indian annual budget in the picture lets understand what it is and who does it. Have questions like What’s an interim budget? What happens in budget?
A national financial interim budget refers to the comprehensive plan outlining a country’s government’s anticipated revenues and planned expenditures for a specific fiscal period, typically a year. This budget serves as a financial roadmap for the nation, guiding the allocation of resources to various sectors and programs in order to achieve economic stability, growth, and meet the needs of the population. We are going to look at the example of Indian interim budget 2024
Key components of a national financial budget include:
- Revenue: This encompasses the government’s expected income from taxes, tariffs, fees, and other sources. It serves as the financial foundation for funding public services and programs.
- Expenditures: Categorized allocation of funds to different sectors such as education, healthcare, defense, infrastructure, social welfare, and more. Each allocation is based on the government’s priorities and policies.
- Deficit or Surplus: The budget may result in either a deficit (when expenditures exceed revenues) or a surplus (when revenues surpass expenditures). Governments may borrow to cover a deficit or save a surplus for future needs.
- Debt Servicing: If the country has outstanding debts, a portion of the budget is allocated to service these debts, including interest payments and principal repayment.
- Economic Assumptions: Economic indicators and assumptions, such as inflation rates, GDP growth projections, and employment figures, which provide context for the budget’s overall feasibility.
- Social and Economic Goals: The budget may outline specific goals and policies to address issues like poverty reduction, unemployment, and economic development.
- Contingency Planning: Provision for unforeseen circumstances or emergencies, ensuring flexibility in the budget to respond to unexpected events.
National budgets are crucial tools for economic management, allowing governments to balance their fiscal responsibilities, foster economic development, and address social and infrastructure needs. Transparency, accountability, and periodic reviews are essential aspects of effective national budgeting to ensure that the allocated resources align with the country’s overall economic and social objectives.
As an example lets look at the financial budget that was presented recently in 2024 – Budget 2024 time is here. Lets explore current scenario and the budget presented recently.
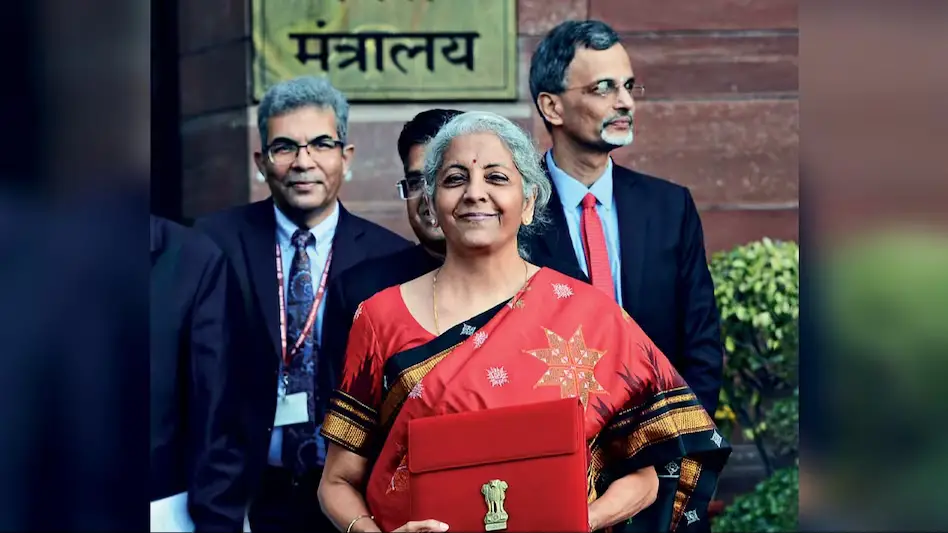

Finance Minister N Sitharaman presented the Interim Budget in the Lok Sabha today, following the Union Cabinet’s approval earlier in the morning.
During her Budget speech, Ms. N Sitharaman emphasized the government’s various programs aimed at women, youth, and the economically disadvantaged. She highlighted the significant transformation witnessed in the Indian economy and the implementation of structural reforms. The government’s focal point, she noted, revolved around four key sectors: women, youth, the economically disadvantaged, and farmers, emphasizing that the country’s progress is intertwined with their advancement.
Key highlights from the Budget speech include:
- Over the past decade, the government lifted 25 crore people out of poverty, while also providing free food to 80 crore individuals through various schemes.
- Direct Benefit Transfers amounting to Rs. 34 lakh crore through PM Jan Dhan Yojana accounts resulted in savings of ₹2.7 lakh crore.
- Schemes like PM Vishwakarma Yojana and PM-SVANidhi provided credit assistance to artisans and street vendors respectively, benefitting millions.
- The government prioritized upskilling and reskilling, training over 1.4 crore youth under the Skill India Mission and sanctioning 43 crore loans under PM Mudra Yojana.
- Initiatives such as the ‘Lakhpati Didi’ scheme aim to empower rural women and bolster the rural economy.
- Emphasis was placed on developing the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor and fostering growth in Eastern regions.
- Measures to address inflation, enhance economic growth, subsidize affordable housing construction, and improve healthcare were outlined.
- Schemes to support agriculture, dairy farming, oilseed self-reliance, and fisheries were proposed.
- The establishment of a new department, Matsya Sampada, to address fishermen’s needs was announced.
- Plans for railway infrastructure upgrades, including converting 40,000 rail bogeys to Vande Bharat standards, were disclosed.
- Initiatives to achieve Net Zero by 2070 through renewable energy, e-vehicle sector expansion, and capital expenditure increases were detailed.
- Fiscal measures included maintaining tax rates, reducing fiscal deficit to 4.5% in 2025-26, and lowering government borrowings for 2024-25.
These highlights represent the government’s commitments and strategies to steer India’s economic trajectory towards sustainable growth and inclusivity.
Let’s understand what an interim budget it
An interim budget is a temporary financial plan presented by a government during a transitional period, often when a new administration is about to assume office or during an election year. This budget serves as a provisional measure to address immediate financial needs until a comprehensive budget is introduced by the newly elected government.
Key characteristics of an interim budget include:
- Temporary Nature: An interim budget is not intended to cover the entire fiscal year. Instead, it addresses immediate financial requirements until a regular budget is formulated and presented.
- Routine Expenditures: It typically focuses on routine government expenditures such as salaries, ongoing projects, and essential services. Major policy changes or the introduction of new initiatives are usually avoided in interim budgets.
- Limited Scope: Interim budgets tend to have a limited scope, primarily addressing urgent financial matters without delving into long-term strategies or significant shifts in economic policies.
- Continuity: The aim of an interim budget is to ensure the continuity of essential government functions and prevent a financial vacuum during a transitional period. It allows for the smooth functioning of public services until a new government can thoroughly assess and plan for the fiscal year.
In short, a financial interim budget serves as a short-term financial plan to sustain government operations and meet immediate financial obligations until a more comprehensive and strategic budget can be formulated by the incoming government.
So why is an interim budget important for people of the nation?
A financial interim budget is important for the people of a nation for several reasons:
- Continuity of Government Operations: An interim budget ensures the smooth functioning of essential government operations and services during a transitional period, such as a change in government or an election year. This continuity is crucial for maintaining public services, infrastructure projects, and government functions without interruptions.
- Financial Stability: The interim budget provides financial stability by addressing routine expenditures, including salaries, ongoing projects, and essential services. This helps prevent disruptions in public services and ensures that government employees continue to receive their salaries and benefits.
- Avoiding Financial Gaps: Without an interim budget, there could be a financial gap between the expiration of the previous budget and the presentation of a new one. This gap could lead to uncertainties, delays in public services, and financial challenges for both the government and the people.
- Infrastructure and Development Projects: Interim budgets often allocate funds for ongoing infrastructure and development projects. This ensures that critical projects are not halted, promoting economic growth and benefiting the public through improved infrastructure.
- Social Welfare Programs: Interim budgets may include provisions for social welfare programs, ensuring that essential services for vulnerable populations, such as healthcare, education, and social assistance, continue without interruption.
- Economic Confidence: The announcement of an interim budget helps maintain economic confidence by signaling stability and continuity in government policies. This confidence is essential for businesses, investors, and the general public, contributing to overall economic stability.
- Preventing Uncertainty: Interim budgets help prevent uncertainty and speculation about government spending and priorities. By addressing immediate financial needs, they provide a clear financial direction until a more comprehensive budget is formulated.
- Policy Direction: While interim budgets typically avoid major policy changes, they may still reflect the priorities and direction of the government in the short term. This can provide insights into the government’s stance on key issues, giving the public an idea of what to expect in the coming fiscal year.
In short, an interim budget plays a vital role in maintaining stability, preventing financial gaps, and ensuring the continued provision of essential services and projects, ultimately benefiting the people of the nation.
Compare two budget types
Lets compare Union Budget to Interim Budget on different aspects
| Aspect | Union Budget | Interim Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Scope and Duration | Comprehensive, covering the entire fiscal year | Temporary, addressing immediate financial needs until a full-fledged budget is presented by the new government or post-election. |
| Policy Changes | May introduce significant policy changes | Typically avoids major policy changes and focuses on routine expenditures. |
| New Initiatives | Introduces new schemes and initiatives | Limited introduction of new initiatives, primarily addressing ongoing projects and essential services. |
| Long-Term Planning | Focuses on long-term economic planning | Serves as a stopgap, focusing on short-term financial stability and continuity. |
| Allocations | Allocates funds for the entire fiscal year | Addresses immediate financial needs without delving into long-term allocations. |
| Impact on Taxation | May introduce changes in tax policies | Generally maintains existing tax rates, avoiding significant changes. |
| Economic Indicators | Presents economic indicators and forecasts | May provide an update on economic conditions but with a shorter-term perspective. |
| Infrastructure Projects | Allocates funds for various projects | Focuses on continuing ongoing projects, avoiding the initiation of major new projects. |
| Social Welfare Schemes | Introduces or modifies social welfare programs | Maintains existing programs, with limited changes to allocations. |
| Duration of Presentation | Full-fledged presentation | Concise presentation, addressing immediate financial concerns. |
This comparison highlights the key differences between a Union Budget and an Interim Budget in terms of their scope, duration, policy changes, and overall focus. The Union Budget typically sets the tone for the entire fiscal year, while an Interim Budget acts as a temporary measure to ensure financial stability during transitional periods.
What to look for
When observing the budget, common people should pay attention to several key aspects that directly impact their lives. Here are some crucial factors to watch for:
- Tax Policies: Check for any changes in income tax rates, exemptions, or deductions. This directly affects the disposable income of individuals and can impact personal finances.
- Social Welfare Programs: Look out for announcements related to social welfare schemes, such as healthcare, education, and poverty alleviation. Changes in allocations to these programs can have a direct impact on the well-being of the common citizens.
- Infrastructure Development: Assess the allocation of funds for infrastructure projects. Increased investments in areas like roads, transportation, and public amenities can improve living standards and boost economic activity.
- Job Creation Initiatives: Examine policies and initiatives aimed at job creation. Job opportunities and employment-related measures are crucial for the economic well-being of the common people.
- Inflation and Price Stability: Monitor the budget’s approach towards controlling inflation and ensuring price stability. This influences the cost of living and the purchasing power of individuals.
- Healthcare and Education Spending: Check for allocations to healthcare and education sectors. Investments in these areas contribute to a healthier and more educated population, fostering long-term societal development.
- Housing and Real Estate Policies: Observe any announcements related to housing schemes and real estate. Policies that facilitate affordable housing can benefit a large section of the population.
- Farmers and Agriculture Sector: Assess the budget’s provisions for the agriculture sector. Support for farmers, irrigation projects, and agricultural infrastructure can impact food production and rural livelihoods.
- Technology and Digital Initiatives: Pay attention to initiatives promoting technology and digitization. These measures can enhance accessibility to services, financial inclusion, and overall efficiency.
- Environmental Sustainability: Look for policies addressing environmental concerns. Measures promoting sustainability and green initiatives are essential for a better quality of life and a sustainable future.
- Education and Skill Development: Check for initiatives supporting education and skill development programs. A focus on education and skill enhancement contributes to a more skilled and competitive workforce.
- Government Debt and Fiscal Deficit: Monitor the government’s approach towards managing debt and controlling the fiscal deficit. Responsible fiscal policies contribute to overall economic stability.
By staying informed about these aspects, common people can better understand the potential impact of the budget on their lives and make informed decisions. Additionally, it helps foster civic engagement and awareness regarding government policies and priorities.
Conclusion
To conclude an interim budget serves as a crucial bridge between transitional periods, providing a temporary financial framework to sustain essential government functions. As a pragmatic measure, it ensures the continuity of public services, prevents financial uncertainties, and maintains stability during times of change, such as shifts in government or election years. While limited in scope, the interim budget addresses immediate financial needs, offering a glimpse into the government’s short-term priorities and commitments. For citizens, it is a reassurance of ongoing services, financial stability, and a signal of the government’s dedication to sustaining critical projects until a comprehensive budget is formulated. Ultimately, the significance of an interim budget lies in its role as a stabilizing force, ensuring the seamless operation of government functions and the well-being of the people during periods of transition.


![[keyword]](https://learnxyz.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/पोस्टचिम-बंगाल-मतदाता-सूची-2026-जारी-मतदान-को-अंतिम-रूप.jpg)
![[keyword]](https://learnxyz.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/SAG-Infotech-Launches-Gen-GST-Software-Version-20-for-Easier.jpg)