In the dynamic world of business, an invoice is more than just a document. It’s a fundamental part of maintaining smooth operations, ensuring proper financial management, and fostering transparent relationships between sellers and buyers. At its core, an invoice is a detailed record of a transaction between two parties, specifying what goods or services were provided, their cost, and the terms of payment. It plays a pivotal role in tracking revenue, ensuring legal compliance, and supporting effective communication between businesses and their clients.
Invoices come in various forms, ranging from traditional paper-based formats to highly advanced electronic invoices. They are essential not only for businesses but also for freelancers and professionals offering their services. Whether you’re an entrepreneur starting a new venture or a seasoned business owner looking to streamline your processes, understanding invoices is crucial to managing finances effectively.
This comprehensive article will dive into all aspects of invoices, from their components and types to their benefits and exclusive facts. We’ll also explore the frequently asked questions surrounding this indispensable business tool. By the end, you’ll have a holistic understanding of what invoices are, why they’re critical, and how they can drive success in your financial management practices.
Contents
Perspective of Invoices in the Indian Context
Top 10 Exclusive Facts About Invoices.

PHILIPS Air Fryer HD9200/90, uses up to 90% less fat, 1400W, 4.1 Liter, with Rapid Air Technology (Black), Large
Price after 35% discount
₹6,499
What Is an Invoice?
An invoice is a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing the products or services provided and the amount owed. It serves as a formal request for payment and includes information such as:
- Invoice number: A unique identifier for tracking purposes.
- Date of issue: The date the invoice is created.
- Description of goods or services: A detailed list of what was sold or provided.
- Payment terms: Specifies the due date and acceptable payment methods.
- Total amount due: Includes all charges, taxes, and applicable discounts.
Invoices act as legal records, ensuring clarity and accountability in financial transactions. They’re also used for tax purposes and help businesses monitor cash flow.

Brief History of Invoices
The practice of documenting transactions dates back thousands of years. In ancient Mesopotamia, clay tablets were used to record trades and financial agreements. These records served a dual purpose: ensuring transparency between trading parties and establishing evidence in case of disputes. Over time, the practice evolved, and by the Middle Ages, merchants used written bills of exchange to track and formalize transactions.
Invoices became indispensable with the rise of commerce and trade during the Industrial Revolution. Businesses required a formal mechanism to document their dealings, particularly as trade extended across cities, countries, and continents. The development of legal frameworks and tax systems further emphasized the need for accurate records. Invoices provided this structure, acting as proof of transaction, a basis for tax computation, and a way to maintain financial records.
In modern times, the digital age transformed invoicing. Electronic and automated invoices have revolutionized the way businesses operate, reducing errors, speeding up processes, and cutting costs. Regardless of technological advancements, the fundamental purpose of invoices remains the same: ensuring accountability, transparency, and efficiency in financial transactions.
Perspective of Invoices in the Indian Context
In India, invoices hold special significance due to the country’s complex taxation system. The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017 marked a significant shift, standardizing taxation across the nation and streamlining the invoicing process.
Importance of Invoices Under GST:
- Tax Compliance: Every business registered under GST is required to issue invoices for taxable goods or services, ensuring proper tax calculation and reporting.
- ITC Claims: Input Tax Credit (ITC), which allows businesses to claim refunds on GST paid for goods or services used in production, is only possible with valid invoices.
- Standardized Format: GST-compliant invoices must include specific details like GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number), HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes, and the tax breakup.
In India, businesses have also embraced e-invoicing under GST, which mandates businesses with specific turnover thresholds to generate invoices through a centralized government portal. This ensures real-time reporting to tax authorities and reduces tax evasion.
Sample Invoice with GST and SGT
Here is a sample invoice for a GST-compliant transaction in India:
XYZ Enterprises
123, Business Avenue, Mumbai, Maharashtra, 400001
GSTIN: 27XXXXXXXXXXXZ5
Invoice No: INV-20250120
Invoice Date: 20-Jan-2025
Due Date: 27-Jan-2025
Bill To:
ABC Retailers
45, Market Road, Delhi, 110001
GSTIN: 07XXXXXXXXXXXC2
Description of Goods/Services:
| S.No | Item Description | HSN Code | Quantity | Unit Price (₹) | Amount (₹) |
| 1 | Premium Office Chair | 94033010 | 5 | 5,000.00 | 25,000.00 |
Subtotal: ₹25,000.00
Taxes:
- CGST (9%): ₹2,250.00
- SGST (9%): ₹2,250.00
Total Payable (₹): ₹29,500.00
Terms & Conditions:
- Payment due within 7 days of invoice date.
- Late payments will incur a penalty of 2% per month.
- Goods once sold cannot be returned.
This sample highlights key elements of an invoice under the GST regime, including HSN codes and a clear breakup of CGST and SGST. Let me know if you’d like further details or enhancements!
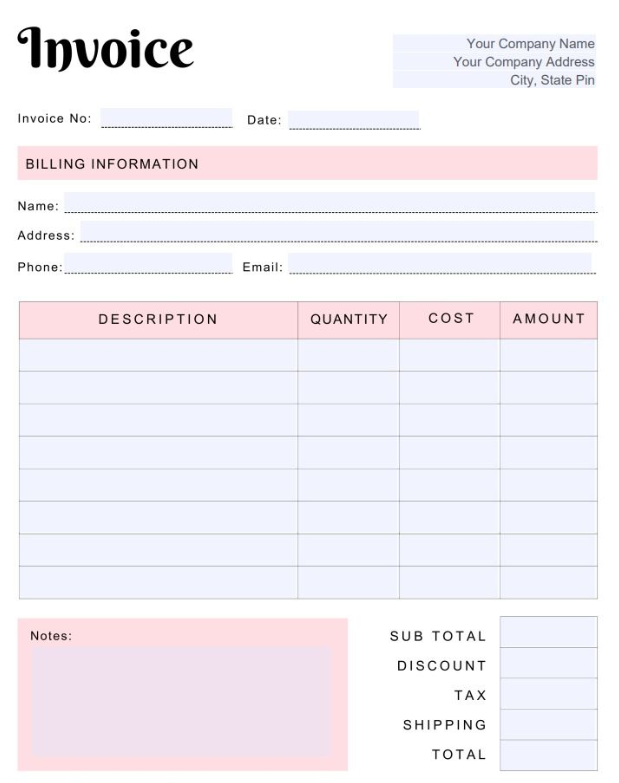
Types of Invoices
There are several types of invoices tailored to different business needs, including:
- Standard Invoice: The most common type, used for straightforward transactions.
- Proforma Invoice: A preliminary bill sent before goods or services are delivered.
- Recurring Invoice: Used for ongoing services, such as subscriptions or retainers.
- Credit Invoice: Issued for refunds or discounts.
- Debit Invoice: Sent when additional charges are applied to a transaction.
- Timesheet Invoice: Used by freelancers or consultants to bill for hours worked.
- Commercial Invoice: Utilized for international trade, including customs details.
- E-Invoice: Digital invoices sent electronically, often integrated with accounting software.
Benefits of Using Invoices
1. Financial Organization: Invoices provide a clear record of income and expenses, simplifying bookkeeping and tax filing.
2. Legal Compliance: They act as proof of transactions, ensuring transparency and adherence to tax laws.
3. Professionalism: Sending detailed invoices reflects a business’s professionalism and helps build trust with clients.
4. Cash Flow Management: Invoices specify payment deadlines, helping businesses plan and maintain a healthy cash flow.
5. Dispute Resolution: A well-documented invoice can prevent or resolve disputes regarding payments or services rendered.
6. Automation Benefits: Modern invoicing tools automate processes, reducing errors and saving time.
Top 10 Exclusive Facts About Invoices
- Historical Roots: The concept of invoicing dates back to ancient Mesopotamia, where clay tablets were used as transactional records.
- First Electronic Invoice: The first e-invoice was introduced in the 1970s, paving the way for digital financial management.
- Global Standards: The United Nations developed the UN/EDIFACT standard for electronic invoicing in international trade.
- Environmental Impact: E-invoices save approximately 80% of the resources used for paper invoices.
- Late Payment Costs: Businesses worldwide lose billions annually due to late payments on invoices.
- Tax Audits: Well-maintained invoices are often the first documents requested during tax audits.
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology is now being integrated into invoicing for enhanced security and transparency.
- Invoice Factoring: Companies can sell unpaid invoices to factoring companies for immediate cash flow.
- Freelancer Adoption: Over 90% of freelancers use invoices to ensure timely payment for their work.
- AI Invoicing: Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing invoicing by automating creation, sending, and follow-ups.

FAQs About Invoices
- What is the purpose of an invoice?
The primary purpose of an invoice is to document a transaction and request payment for goods or services rendered.
- What should an invoice include?
An invoice should include the seller’s details, buyer’s details, invoice number, date of issue, description of goods or services, payment terms, and the total amount due.
- Are invoices legally binding?
Yes, invoices are legally binding documents, provided they include all necessary details and are acknowledged by both parties.
- What’s the difference between an invoice and a receipt?
An invoice is a request for payment, while a receipt is proof that payment has been made.
- How do e-invoices work?
E-invoices are created digitally and sent electronically, often through invoicing software or platforms.
- Can invoices be used for tax purposes?
Yes, invoices are crucial for tax filing as they provide a record of income and expenses.
- What are recurring invoices?
Recurring invoices are automated invoices sent regularly for ongoing services, such as subscriptions.
- What is invoice factoring?
Invoice factoring involves selling unpaid invoices to a factoring company in exchange for immediate cash.
- How long should invoices be kept?
Invoices should be retained for at least 6-7 years, depending on local tax laws.
- What is an overdue invoice?
An overdue invoice is one that has not been paid by the specified due date.
- Are digital signatures valid on invoices?
Yes, digital signatures are legally valid on invoices in many countries.
- How can I prevent invoice fraud?
Use secure invoicing software, verify client details, and regularly monitor financial transactions.
- What is the GST on invoices?
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a tax included on invoices in many countries, specifying the tax amount charged.
- Can an invoice be canceled?
Yes, canceled invoices should be marked as void and documented accordingly.
- How does invoicing software help?
Invoicing software streamlines the process by automating creation, sending, tracking, and storing invoices.
- What is the difference between a proforma invoice and a standard invoice?
A proforma invoice is a preliminary document, while a standard invoice is a final request for payment.
- What happens if a client doesn’t pay an invoice?
Unpaid invoices may lead to follow-ups, late fees, or legal action if necessary.
- Are there penalties for incorrect invoices?
Yes, incorrect invoices may lead to disputes, late payments, or penalties during tax audits.
- Can invoices be customized?
Yes, invoices can be tailored to include branding, specific terms, and additional details as required.
- What are invoice payment terms?
Payment terms specify when and how a payment should be made (e.g., Net 30 means payment is due within 30 days).
- What is an invoice template?
An invoice template is a pre-designed format that simplifies the creation of invoices.
- Are there laws governing invoicing?
Yes, invoicing is regulated by local and international laws to ensure transparency and compliance.
- Can invoices include discounts?
Yes, discounts can be mentioned on invoices, specifying the amount reduced from the total.
- What is a tax invoice?
A tax invoice includes details of applicable taxes, such as VAT or GST, and is issued for tax compliance.
- How can I ensure timely invoice payments?
Set clear terms, send reminders, and offer multiple payment options.
- Can I issue an invoice in advance?
Yes, proforma invoices are issued in advance for estimated amounts.
- What is a zero-rated invoice?
A zero-rated invoice applies to goods or services exempt from tax, with a 0% tax rate.
- How do businesses track unpaid invoices?
Unpaid invoices can be tracked using accounting software or manual records.
- What is the role of a purchase order in invoicing?
A purchase order is a buyer’s request for goods/services, often referenced in the corresponding invoice.
- Are handwritten invoices acceptable?
Yes, handwritten invoices are acceptable but less common due to modern digital alternatives.
Conclusion
Invoices are the lifeblood of any business transaction. From small startups to multinational corporations, they provide structure, accountability, and transparency. A well-crafted invoice ensures smooth financial operations, promotes trust between parties, and guarantees legal compliance. With technological advancements, invoicing has evolved significantly, offering more efficient and eco-friendly options like e-invoicing and AI-powered automation.
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, the role of invoices becomes even more critical. They’re not just about payments; they’re about maintaining professional relationships, enabling cash flow management, and supporting strategic growth.
Whether you’re issuing a simple invoice for a single transaction or managing a complex invoicing system for international trade, understanding the nuances of invoicing will set your business on the path to success. Stay proactive, embrace modern tools, and ensure every invoice reflects professionalism and accuracy. After all, the foundation of every thriving business is built on clear and efficient financial communication.
Good Reads