NOTE: This blog has been updated to announce support for additional supported third-party model providers for the Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant. Additional testing and validation of new model providers is ongoing. For the most recent list of supported model vendors, Please refer to Red Hat’s official documentation.
Earlier this year, we released the Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant, a generative AI service that provides an intuitive chat assistant embedded in Ansible Automation Platform. The Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant is like having an Ansible expert at your keyboard. The service integrates documentation directly into the Ansible administration and operations experience for faster troubleshooting and onboarding, as well as support for the day-to-day management of your automation itself.
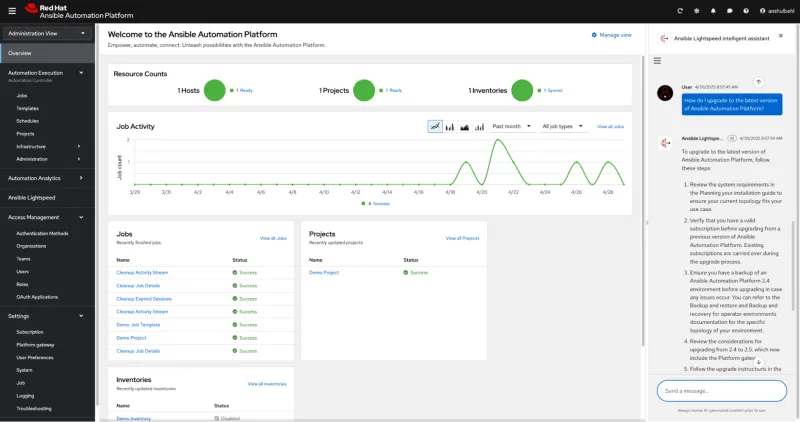
Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant within Ansible Automation Platform
This generative AI service is the result of a concerted effort by our product and engineering teams to improve the overall platform user experience for both automation administrators and IT operators. Examples include a simplified and unified UI, the release of self-service automation to empower more users, a new on-site analytics dashboard to measure performance, a fleet of new collections for managing the platform, and more.
Extending generative AI within the Ansible Automation Platform user experience
When we initially launched Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant In 2023, its goal was to provide a robust coding assistant designed to help boost engineer and developer productivity during the creation of Ansible content, including playbooks, roles, or tasks. We later embedded features such as content clarification and content source matching for greater transparency and context for model responses as well as rapid refinement. Leveraging IBM’s Granite code models and trained on Ansible-specific data sources, the Coding Assistant democratizes access to automation and helps onboard new users as they familiarize themselves with the Ansible language and syntax.
With the intelligent assistant, we bring similar value to Ansible Automation Platform administrators and operators by reducing friction and swivel-chair operations, allowing these users to stay within the platform experience to research, troubleshoot and resolve common questions and issues.
The intelligent assistant can respond to requests such as:
- “What is an execution environment?”
- “How do I manage user access to Ansible Automation Platform?”
- “Explain the “ERROR! could not resolve module/action” error message?”
- “How do I configure Event-Driven Ansible?”
The use of a recycling increased generation (RAG) pipeline linked to Red Hat documentation and other resources, the intelligent assistant also provides referenced links to additional documentation to help you explore a given topic in more detail.
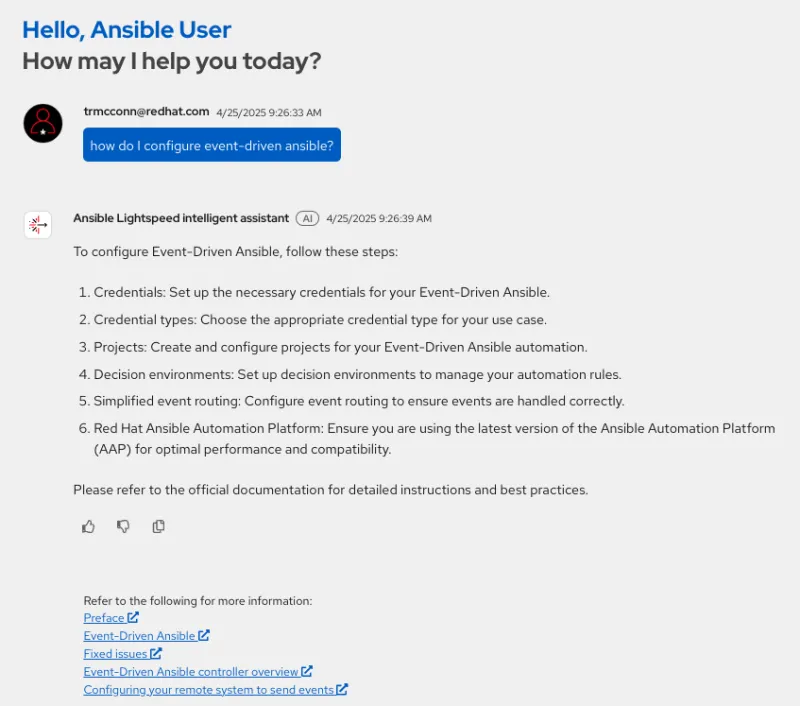
Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant fast, responsive, and referenced resources
Additional roadmap items for the intelligent assistant include expanding data sources to provide visibility into the health and performance of your automation itself. For example, you will be able to get help with assignments such as:
- “Why did my automation ‘VM migration’ job fail?”
- “Show me all inventory included in my Ansible Automation Platform deployment.”
- “What is the status of all jobs currently running and their progress?”
Getting started with Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant
To set up the Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant for your users, you will need:
- An active subscription to Ansible Automation Platform
- Deployment of an LLM served on a Red Hat AI or by bringing your own model with any currently supported configurations listed in Red Hat documentation.)
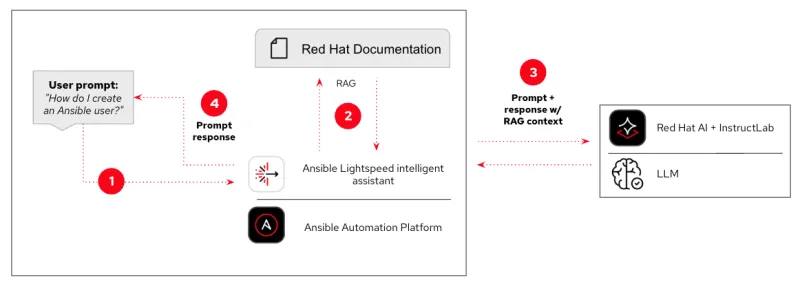
For more information on installing and configuring Ansible Lightspeed intelligent assistant, please refer to our documentation.


![[keyword]](https://learnxyz.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Measure-business-impact-with-Dashboard-and-Analytics.jpg)

![[keyword]](https://learnxyz.in/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/Fix-broken-updates-uCareSystem-new-release-uCareSystem-v2512.jpg)
