Obesity is a chronic health condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the body, which can have serious implications for overall health and well-being. In recent years, obesity has become a global epidemic, affecting millions of people across different age groups, socioeconomic backgrounds, and geographic regions. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), worldwide obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, with an increasing number of children and adults struggling with weight-related issues. While some people may associate obesity solely with lifestyle choices, it is important to recognize that obesity is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, environment, psychological well-being, and metabolic conditions.
The rise in obesity rates can be attributed to various factors, such as increased consumption of calorie-dense foods, sedentary lifestyles, stress, lack of sleep, and limited access to nutritious foods. The widespread availability of processed foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates has contributed significantly to the obesity crisis. Additionally, modern-day conveniences, such as desk jobs, digital entertainment, and the increased use of automobiles, have led to decreased physical activity, further exacerbating the issue.
Obesity is not merely a cosmetic concern; it is associated with a wide range of serious health complications, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, stroke, certain cancers, and respiratory disorders. Moreover, obesity can impact mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Given the significant health and social burdens associated with obesity, it is imperative to take proactive measures to prevent and manage this condition effectively.
Addressing obesity requires a multifaceted approach that involves lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, regular physical activity, and, in some cases, medical interventions. By understanding the root causes of obesity and implementing sustainable lifestyle changes, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy weight. This article explores the causes, consequences, and effective strategies for tackling obesity, including practical diet plans and exercise routines that promote long-term well-being.
Contents
Effective Ways to Tackle Obesity.
Diet Plans for Tackling Obesity.
Defining Obesity
Obesity is typically assessed using the Body Mass Index (BMI), a measure calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a BMI over 25 is considered overweight, and over 30 is classified as obese. However, BMI does not account for fat distribution or muscle mass, leading to potential misclassifications. Recent discussions among experts suggest revising obesity definitions to consider fat distribution and its impact on organ function and daily life.
Causes of Obesity
The development of obesity is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors:
- Dietary Habits: Consuming high-calorie, energy-dense foods rich in fats and sugars contributes significantly to weight gain. The widespread availability of processed foods and sugary beverages has exacerbated this issue.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles, characterized by minimal physical activity, reduce energy expenditure, leading to an energy imbalance and fat accumulation.
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition can influence how the body stores fat and regulates appetite, making some individuals more susceptible to obesity.
- Socioeconomic Factors: Limited access to healthy foods, safe environments for physical activity, and health education disproportionately affect lower-income populations, increasing obesity risk.
- Psychological Factors: Emotional stress, depression, and certain psychological conditions can lead to overeating and weight gain.
Health Consequences
Obesity is associated with numerous health complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Increased risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excess body fat contributes to insulin resistance, leading to diabetes.
- Certain Cancers: Higher incidence of cancers such as breast, colon, and endometrial cancer.
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Joint problems and osteoarthritis due to increased load on joints.
- Respiratory Issues: Sleep apnea and other breathing difficulties.
- Mental Health Conditions: Depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
Effective Ways to Tackle Obesity
Managing and overcoming obesity requires a holistic approach that incorporates healthy habits, behavioral changes, and medical guidance when necessary. Here are some effective ways to tackle obesity:
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Eating a well-balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates is essential for weight management. Avoiding processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive salt intake can significantly contribute to weight loss and improved health.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Exercise plays a crucial role in burning calories and improving metabolism. Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, and strength training can help individuals lose weight and maintain a healthy body composition.
- Monitor Portion Sizes: Controlling portion sizes prevents overeating and allows for better regulation of caloric intake. Using smaller plates, measuring food portions, and being mindful while eating can help individuals avoid unnecessary weight gain.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking sufficient water throughout the day helps control appetite, improve metabolism, and support overall bodily functions. Replacing sugary drinks with water can reduce excess calorie intake and contribute to weight loss.
- Improve Sleep Patterns: Poor sleep can contribute to weight gain by affecting hunger hormones and increasing cravings for unhealthy foods. Prioritizing quality sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can positively impact weight management.
- Manage Stress Levels: Chronic stress can lead to emotional eating and weight gain. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and spending time outdoors can help maintain a healthy mindset and prevent stress-related overeating.
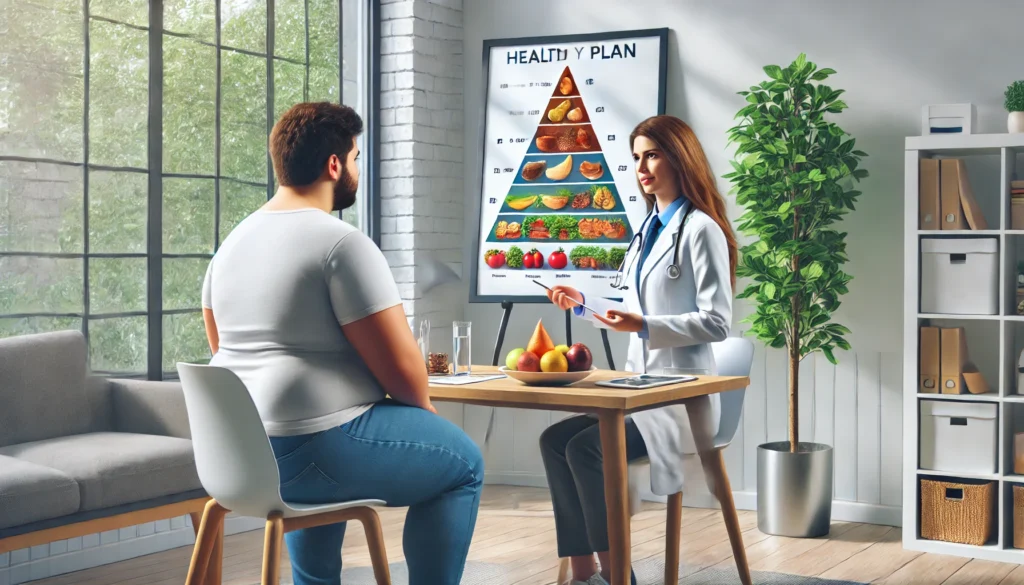
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting a registered dietitian, nutritionist, or healthcare provider can help individuals develop personalized weight loss plans tailored to their needs. Medical professionals can also recommend appropriate medications or surgical interventions for severe cases of obesity.
Diet Plans for Tackling Obesity
Creating a sustainable diet plan is essential for effective weight management. Below are some diet plans that can help individuals combat obesity:
- Mediterranean Diet: This diet emphasizes whole foods, healthy fats, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. It promotes heart health and weight loss by reducing processed foods and incorporating nutrient-dense meals.
- Low-Carb Diet: Reducing carbohydrate intake, particularly refined carbs and sugars, can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote fat loss. Diets such as the ketogenic diet or Atkins diet focus on increasing healthy fats and proteins while limiting carb consumption.
- Plant-Based Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains can help reduce calorie intake and support weight loss. Plant-based diets are also associated with lower risks of chronic diseases.
- Intermittent Fasting: This eating pattern involves alternating between periods of eating and fasting, which can help control calorie intake and improve metabolic health. Popular methods include the 16:8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window) and the 5:2 method (eating normally for five days and consuming fewer calories for two days).
- DASH Diet: Originally designed to lower blood pressure, the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet focuses on whole foods, lean proteins, and reducing sodium intake. It supports weight loss while promoting heart health.

Global Prevalence
Obesity rates have been rising globally, with significant variations across regions:
- Global Trends: From 1990 to 2022, the percentage of adults living with obesity more than doubled from 7% to 16%.
- Youth Obesity: The percentage of children and adolescents aged 5–19 years living with obesity increased four-fold from 2% to 8% globally during the same period.
- Future Projections: By 2050, it is estimated that over half of the adult population and nearly a third of children and young people will be overweight or obese, totaling more than 3.8 billion adults and 746 million youths.
Management and Treatment
Addressing obesity requires a comprehensive approach:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, coupled with regular physical activity, is foundational.
- Behavioral Therapy: Counseling and support groups can help individuals develop healthier eating habits and coping mechanisms.
- Medications: Prescription medications may assist in weight loss by reducing appetite or fat absorption.
- Surgical Interventions: Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass, is considered for individuals with severe obesity, leading to significant and sustained weight loss.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing obesity involves individual and societal efforts:
- Public Health Policies: Implementing regulations to limit the marketing of unhealthy foods, taxing sugary beverages, and ensuring access to nutritious foods.
- Community Programs: Creating environments that promote physical activity, such as parks and recreational facilities.
- Education: Raising awareness about healthy lifestyle choices through schools and media campaigns.
Top 15 FAQs on Obesity
What is obesity?
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation that increases the risk of various health problems. It is typically measured using the Body Mass Index (BMI), with a BMI of 30 or higher considered obese.
What causes obesity?
Obesity is caused by a combination of factors, including poor diet, lack of physical activity, genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, and lifestyle habits. Psychological factors like stress and depression can also contribute.
How is obesity diagnosed?
Obesity is diagnosed primarily using BMI, waist circumference, and body fat percentage. A BMI above 30 is classified as obese, and additional tests may be conducted to assess related health risks.
What are the health risks associated with obesity?
Obesity increases the risk of serious health conditions, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, certain cancers, sleep apnea, and joint problems like osteoarthritis.
Is obesity genetic?
Genetics can influence obesity, but lifestyle choices play a crucial role. Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to store more fat, but diet and exercise significantly impact weight management.
Can obesity be prevented?
Yes, obesity can be prevented through a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle from an early age.
What are the best treatments for obesity?
Treatment options include lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, physical activity, behavior therapy, medication, and, in severe cases, weight-loss surgery (bariatric surgery).
What are the best diets for weight loss?
Effective diets include the Mediterranean diet, low-carb diet, intermittent fasting, plant-based diet, and the DASH diet. Each focuses on reducing processed foods and increasing whole, nutrient-dense foods.
Does exercise alone help in weight loss?
While exercise is important, diet plays a larger role in weight loss. A combination of both diet and regular physical activity is the most effective approach to losing and maintaining weight.
Can obesity affect mental health?
Yes, obesity is linked to mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and body image concerns. Social stigma can further impact psychological well-being.
Are there medications for obesity?
Yes, doctors may prescribe medications like Orlistat, Phentermine, or GLP-1 receptor agonists for weight loss, but they should be used under medical supervision alongside lifestyle changes.

What are the surgical options for obesity?
Bariatric surgery, including gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding, is available for individuals with severe obesity who have not responded to other treatments.
Can obesity be reversed?
Yes, obesity can be managed and even reversed through consistent lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet, exercise, behavioral therapy, and medical interventions if necessary.
How long does it take to lose weight effectively?
Weight loss varies by individual, but a safe and sustainable rate is 1-2 pounds per week through diet and exercise. Rapid weight loss can be unhealthy and difficult to maintain.
How does sleep affect obesity?
Poor sleep disrupts hormones that regulate appetite, leading to increased cravings and weight gain. Ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep is essential for weight management.
Conclusion
Obesity is a pressing public health concern that requires immediate attention and action. It is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, socioeconomic status, and psychological well-being. With obesity rates continuing to rise, the need for effective prevention and management strategies has never been greater.
The consequences of obesity extend far beyond physical health. It affects emotional well-being, social interactions, and overall quality of life. Individuals struggling with obesity often face stigma and discrimination, which can further impact their mental health and motivation to seek help. By fostering a more supportive and inclusive environment, society can encourage individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles without the fear of judgment.
Preventing and managing obesity requires a commitment to sustainable lifestyle changes, including maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, improving sleep hygiene, and managing stress effectively. Government initiatives, community programs, and workplace wellness efforts can also play a significant role in combating obesity by promoting healthier habits on a larger scale.
While there is no one-size-fits-all solution to obesity, taking proactive steps to improve dietary habits, exercise routines, and mental well-being can make a significant difference. For individuals struggling with severe obesity, medical interventions such as weight loss medications or bariatric surgery may be viable options to achieve long-term health improvements.
Ultimately, addressing obesity is not just about losing weight—it is about enhancing overall well-being and leading a healthier, more fulfilling life. By making informed choices and seeking professional guidance when necessary, individuals can successfully manage their weight and reduce the risks associated with obesity. Through collective efforts from individuals, healthcare professionals, and policymakers, society can create a healthier future and curb the obesity epidemic for generations to come.
Related Good Reads






I truly enjoy reading on this website , it has got great blog posts.